As mentioned, an annuity due differs contribution margin from an ordinary annuity in that the annuity due’s payments are made at the beginning, rather than the end, of each period. FV is a measure of how much a series of regular payments will be worth at some point in the future, given a specified interest rate. You can calculate the present or future value for an ordinary annuity or an annuity due using the formulas shown below. There are several ways to measure the cost of making such payments or what they’re ultimately worth. Read on to learn how to calculate the present value (PV) or future value (FV) of an annuity. As a reminder, this calculation assumes equal monthly payments and compound interest applied at the beginning of each month.
- Unlike lifetime annuities there’s a risk that you may outlive your fixed annuity, leaving you without income in your old age.
- When working with multiple time segments, it is important that you always start your computations on the side opposite the unknown variable.
- This comparison helps you choose the annuity product that best aligns with your financial goals and offers the most favorable terms for your situation.
- However, you cannot easily research subaccount performance through a fund tracker.
💡 Expert-Led Sessions📊 Build Financial Models⏳ 60+ Hours Learning
- The present value can tell you how much you have to invest in an immediate annuity to get payouts of a certain amount, too.
- After all, $10,000 multiplied by 120 months will yield a final payout of $1,200,000, which is $200,000 more than the lump sum payment.
- It shows that $4,329.48, invested at 5% interest, would be sufficient to produce those five $1,000 payments.
- You’ll input details including your current age and tax rate as well as the age and tax rate you’ll be at when you intend to start withdrawing from your annuity.
- Our network of advisors will never recommend products that are not right for the consumer, nor will Annuity.org.
For example, a 50-year-old how to calculate future value of annuity individual may make annual payments on a deferred annuity for 15 years. Since annuities are tax-deffered, they’lll only have to pay taxes on the payouts as received. If you know what the future monthly payments would be worth now, you need to calculate the present value of the annuity. This will tell you the amount of money you would need to have to generate the monthly payments. This comprehensive book provides an in-depth look at various financial concepts, including annuities and their future value. It offers valuable insights into financial calculations and investment strategies.
Interest Rate
All else being equal, the future value of an annuity due will be greater than the future value of an ordinary annuity because the money has had an extra period to accumulate compounded interest. In this example, the future value of the annuity due is $58,666 more than that of the ordinary annuity. Present value tells you how much money you would need now to produce a series of payments in the future, assuming a set interest rate.
Annuity Rates Information
Future value, on the other hand, is a measure of how much a series of regular payments will be worth at some point in the future, given a set interest rate. If you’re making regular payments on a mortgage, for example, calculating the future value can help you determine the total cost of the loan. To account for payments occurring at the beginning of each period, the ordinary annuity FV formula above requires a slight modification.
Hence, 540 payments of $300 at 9% compounded monthly results in a total saving of $2,221,463.54 by the age of retirement. Many insurance companies sell lifetime annuities to retirement-age individuals. Sometimes, lifetime annuities may be transferred to the buyer’s spouse upon the annuity holder’s Accounting for Churches death.

The longer the period, the more payments are made and the more time the investment has to grow, resulting in a higher future value. Conversely, a shorter period results in fewer payments and less time for growth. A fixed annuity is an insurance product that accumulates interest at a fixed rate on a lump sum premium before converting the principal and interest into a guaranteed income stream. The biggest limitation of the fixed annuity calculator is that it cannot predict how a fixed annuity’s interest rate might change over the contract’s term.


With the general formula below, we can solve a variety of problems involving the future value of an annuity. The following table shows how these $1 payments will accumulate to $4.6410 at the end of the fourth period (or, in this case, year). Subject to the provisions of this notice, articles, materials and content published on this site (Annuity.com) are the property of Annuity.com, Inc.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
Below, we can see what the next five months would cost you, in terms of present value, assuming you kept your money in an account earning 5% interest. This slight difference in timing impacts the future value because earlier payments have more time to earn interest. Imagine investing $1,000 on Oct. 1 instead of Oct. 31 — it gains an extra month of interest growth. This formula considers the impact of both regular contributions and interest earned over time. By using this formula, you can determine the total value your series of regular investments will reach in the future, considering the power of compound interest. Imagine you plan to invest a fixed amount, say $1,000, every year for the next five years at a 5 percent interest rate.
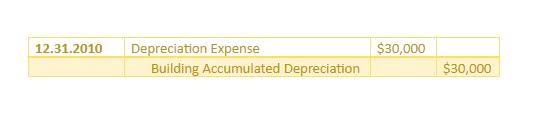
Continuous Compounding (m → ∞)
Or, you can compare the future and present values of an annuity to decide if you want to sell a mature annuity for extra cash flow. If your annuity promises you a $50,000 lump sum payment in the future, then the present value would be that $50,000 minus the proposed rate of return on your money. In this context, an “ordinary annuity” is the same as an immediate fixed annuity, meaning that the holder of the annuity will begin to immediately receive payments for the rest of their life.